Light – A Brief Introduction
Light is a beautiful and essential part of our world. It is the source of all life on Earth, and it gives us the ability to see and experience the world around us. Light can be both gentle and harsh, playful and serious. It can be used to create art, to communicate, and to heal. Light is a powerful force that can both illuminate and transform.
Light is a captivating and essential aspect of our world. We encounter it every day, from the moment the sun rises, casting its warm glow, to the soft illumination of a bedside lamp as we settle down for the night. But have you ever wondered about the fascinating nature of light itself? In this blog post, we will explore the wonders of light, its characteristics, and its impact on our lives.
Table of Contents
What is Light?
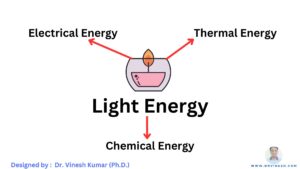
At its core, light is a form of energy that allows us to see and perceive the world around us. It travels in waves, much like ripples on a pond, but at an incredible speed. In fact, light travels so fast that it can circumnavigate the Earth seven and a half times in just one second!
The Colors of Light
One of the most captivating aspects of light is its ability to produce different colors. We are familiar with the colors of the rainbow – red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet. These colors are part of what we call the visible spectrum, the range of colors that our eyes can detect. Each color corresponds to a different wavelength of light, with red having the longest wavelength and violet the shortest.

How Does Light Move?
Light travels in straight lines until it encounters an object or substance that can either reflect or refract it. When light hits a smooth surface, like a mirror, it bounces off and reflects back to our eyes, allowing us to see our reflection. This reflection is what makes mirrors so useful for grooming and checking our appearance.
On the other hand, when light passes through a substance like water or glass, it can change direction. This phenomenon is called refraction. Think about when you place a pencil in a glass of water – it appears to bend or break at the water’s surface. This bending of light is due to refraction.
Light and Shadows
Have you ever noticed how shadows form when an object blocks the path of light? Shadows occur when an object prevents light from reaching a surface. As a result, the area behind the object appears darker compared to the surrounding areas. Shadows can vary in size and shape depending on the position of the light source and the object casting the shadow.
Practical Uses of Light
Light has numerous practical applications in our daily lives. We rely on it for vision, as our eyes capture and process the light that allows us to see the world. Light is also used in various forms of communication, such as fiber optics, where light signals carry vast amounts of information through thin strands of glass or plastic.
Additionally, light plays a vital role in photography. Cameras capture light and convert it into images that preserve moments and memories. Professional photographers often use light creatively, manipulating its intensity, direction, and color to create stunning visual effects.
The Symbolism of Light
Beyond its scientific properties, light holds deep symbolic meaning across cultures and traditions. Light is often associated with knowledge, wisdom, and enlightenment. It represents hope, guiding us through challenging times and illuminating our paths.
In religious and spiritual contexts, light is often considered sacred. It symbolizes divine presence, purity, and spiritual awakening. Candlelight, for example, is used in many religious ceremonies and rituals as a way to invoke a sense of spiritual connection.
Light and Our Well-Being
Light also has a significant impact on our well-being. Exposure to natural light, particularly sunlight, helps regulate our internal body clock and supports our sleep patterns. It boosts our mood, improves productivity, and even plays a role in the synthesis of vitamin D in our bodies.
Appreciating the Beauty of Light
As we ponder the wonders of light, let us take a moment to appreciate its beauty and significance in our lives. Whether it’s the warm glow of a sunset, the twinkle of stars in the night sky, or the delicate dance of fireflies on a summer evening, light surrounds us with its enchanting presence.
So, the next time you gaze at a rainbow or marvel at a stunning sunrise, pause for a moment and reflect on the remarkable phenomenon that is light. Its brilliance and ability to illuminate our world make it truly awe-inspiring. Let us embrace the beauty of light and celebrate its role in shaping our perceptions and enriching our lives.
Learn more about the wonders of light and its impact on our world.
Book on Light:
On a Beam of Light: A Story of Albert Einstein
Facts about how does the light move? :
Light makes things visible.
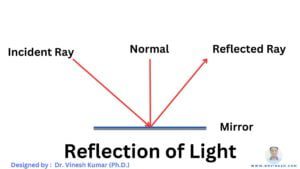
- A mirror changes (reflected) the direction of light that falls on it.
- The light ray, which strikes a mirror or? any surface is called an incident ray while the ray that comes back from the surface after reflection is called reflected ray.
- Normal is the perpendicular line on the mirror where the incident rays strike.
- The angle between the incident ray and the normal is called the angle of incidence.
- According to the first law of reflection, the angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection.
- According to the second law of reflection, the incident ray, the normal at the point of incidence, and the reflected ray all lie in the same plane.

- In an image formed by a mirror the right of the object appears on the left side and the left appears on the right. This phenomenon is called lateral inversion.
- When all parallel incident rays are reflected through an irregular or rough surface the reflected rays are not parallel. This is called irregular or diffused reflection.
- When all parallel incident rays are reflected through a regular or smooth surface the reflected rays are also parallel. This is called regular reflection.
- Reflected light rays can be reflected again after striking with another mirror or surface. This property is used in Periscopes and Kaleidoscope.
- Two mirrors inclined to each other give multiple images.
- Beautiful patterns are formed in a Kaleidoscope because of multiple reflections.
- The main parts of the human eye are the retina, iris, cornea, pupil, lens, and optic nerve.
- At the junction point of the retina and optic nerve, there are no sensory cells, so no vision is possible at that spot. This is called blind spot.
- Visually impaired people can read and write using the Braille system.
- The sunlight (white light) consists of seven colors. The splitting of light into its constituents is called dispersion of light.

Book on Light:
On a Beam of Light: A Story of Albert Einstein
Practice Questions for Competitive Exams
- What is light?
- Light is a form of energy that can travel through space.
- Light is made up of photons, which are tiny particles of light.
- Light can be reflected, refracted, and absorbed by objects.
- Light is essential for life on Earth.
- Answer: A, B, C, and D.
- What are the different types of light?
- Visible light: The light that we can see.
- Infrared light: The light that is below visible light.
- Ultraviolet light: The light that is above visible light.
- X-rays: The light that has a very short wavelength.
- Gamma rays: The light that has the shortest wavelength.
- Answer: A, B, C, D, and E. All option are correct.
- How does light travel?
- Light travels in a straight line.
- The speed of light is 299,792,458 meters per second.
- Light can travel through a vacuum.
- Light can also travel through transparent materials, such as glass and water.
- Answer: A, B, C, and D.
- What is reflection?
- Reflection is the bouncing of light off of a surface.
- The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
- The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
- Reflection can be used to create mirrors and lenses.
- Answer: A, B, C, and D.
- What is refraction?
- Refraction is the bending of light when it passes through a transparent material.
- The refractive index of a material is a measure of how much light bends when it passes through the material.
- The refractive index of water is higher than the refractive index of air.
- This is why a pencil appears to bend when it is placed in a glass of water.
- Answer: A, B, and C.
- What is absorption?
- Absorption is the process by which light is converted into another form of energy, such as heat.
- The color of an object is determined by the wavelengths of light that it absorbs.
- A red object absorbs all of the wavelengths of light except for red light.
- This is why we see the object as red.
- Answer: A, B, and C.
- What is the law of refraction?
- The law of refraction states that the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is constant for a given pair of materials.
- This means that the amount of bending of light is always the same for a given pair of materials.
- The law of refraction can be used to calculate the refractive index of a material.
- Answer: A.
- What is dispersion?
- Dispersion is the separation of white light into its component colors.
- This happens because different colors of light have different refractive indices.
- Red light has the lowest refractive index, followed by orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet.
- This is why a rainbow appears to be made up of different colors.
- Answer: A, B, and C.
- What is a lens?
- A lens is a transparent material that bends light.
- Lenses can be used to focus light, magnify objects, or create images.
- There are two main types of lenses: converging lenses and diverging lenses.
- Converging lenses make objects appear larger.
- Diverging lenses make objects appear smaller.
- Answer: A, B, and C.
- What is a mirror?
- A mirror is a surface that reflects light.
- Mirrors can be used to reflect light, magnify objects, or create images.
- There are two main types of mirrors: plane mirrors and curved mirrors.
- Plane mirrors reflect light in a straight line.
- Curved mirrors reflect light in a curved way.
- Answer: A, B, and C.
- Which of the following is not a property of light?
- It can travel through a vacuum.
- It can be reflected.
- It can be refracted.
- It can be absorbed.
- It can be polarized.
- Answer: D.
- The speed of light in a vacuum is:
- 300,000 kilometers per second.
- 299,792,458 meters per second.
- 186,282 miles per second.
- All of the above.
- None of the above.
- Answer: D.
- The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. This is known as:
- The law of reflection.
- The law of refraction.
- The law of absorption.
- The law of dispersion.
- None of the above.
- Answer: A.
- The refractive index of water is:
- Less than the refractive index of air.
- Equal to the refractive index of air.
- Greater than the refractive index of air.
- None of the above.
- Answer: C.
- The color of an object is determined by:
- The wavelengths of light that it reflects.
- The wavelengths of light that it absorbs.
- The wavelengths of light that it refracts.
- The wavelengths of light that it disperses.
- None of the above.
- Answer: A.
- The law of refraction states that the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is constant for a given pair of materials. This is known as:
- Snell’s law.
- Descartes’ law.
- Fermat’s principle.
- Huygens’ principle.
- None of the above.
- Answer: A.
- Dispersion is the separation of white light into its component colors. This is caused by:
- The different wavelengths of light having different refractive indices.
- The different wavelengths of light having different absorption coefficients.
- The different wavelengths of light having different dispersion coefficients.
- None of the above.
- Answer: A.
- A lens is a transparent material that bends light. The amount of bending of light by a lens is determined by:
- The refractive index of the lens material.
- The curvature of the lens.
- The thickness of the lens.
- All of the above.
- None of the above.
- Answer: D.
- A mirror is a surface that reflects light. The amount of reflection of light by a mirror is determined by:
- The smoothness of the mirror surface.
- The angle of incidence of the light.
- The wavelength of the light.
- All of the above.
- None of the above.
- Answer: D.
- The image formed by a plane mirror is:
- Upright.
- Virtual.
- Same size as the object.
- All of the above.
- None of the above.
- Answer: A, B, and C.
Support Us: Support our cause and make a contribution through UPI payment methods like Google Pay, Phone Pay, or Paytm. Your support goes a long way in helping us make a positive impact.
UPI Payment (Google Pay/Phone Pay/Paytm)

Read also
CTET Exam 2023: Exam Date, Paper Format and Eligibility
College Admission Process in India: A Roadmap to Higher Education
After Admission Problems of a Student
How to Best Utilize Your Study Holidays: 15 Effective Ways
Career Options after Graduation in 2023: Exploring the Pathways to Success
12 Easy Tips to Study Consistently for long hours
How to Make Science Projects: A Step-by-Step Guide
Best Stationary Items for Students: All Essentials for Academic Success
Front Page for Projects: Making a Powerful First Impression
First Aid Beauty: Your Go-To Guide for Effective Skincare Solutions.
What is a Mole in Chemistry: The Remarkable Significance of the Mole
Types of Sentences: Unlock Diversity of Sentence Structures with Worksheet
How to Get Good Grades in Exams: A Comprehensive Guide
Significant Figures: Boost and unlock your 360 Degree performance
How to Score Full Marks in Exams: 6 Proven Strategies
How to study chemistry? 17 Proven Strategies to Master Chemistry
Best Reference Books For Class 10 CBSE Students
Types of Sentences: Unlock Diversity of Sentence Structures with Worksheet
The 8 Parts of Speech: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding English Language
General Knowledge Questions with answers Part-1: Journey into the Unknown
General Knowledge Questions with Answers Part-2: Ignite Your Mind